I recently watched trailer of "Jurassic World", where scientists are again cloning DNA of thousands years old dinosaur.
Let refresh our memory and see how the word cloning fit into Java world.
What is cloning ?
"In biology, cloning is the process of producing similar populations of genetically identical individuals that occurs in nature when organisms."
-- Wikipedia
Here the term "genetically identical" need attention for Java developers for doing cloning of objects. We will look into the details later.
Java provide a method which help us to create "genetically identical" copy of object. It is achieved through clone() method, which is inside Object class.
Now lets see why Java provide a method to create object. If we create a new object then the state of the object is initialized, but what if we need a current state of object but at the same time we didn't want to disturb the current object.
For Example :-
Suppose you have an object X which is a singleton object and shared across application. In this scenario suppose a module need an object of X which will be changed the state of the object temporally but this will affect other module also. In this kind of scenario we need a clone of object.
How to clone an object ?
We can clone only those classes object which implements the Cloneable interface else it will result into CloneNotSupportedException exception.
Cloneable interface is a markup interface like Serializable interface. Cloneable interface is used to indicate that a class allows a bit wise copy of an object to be made.
Please note clone method does not invoke the constructor of target.
Simple example of Cloning.
Let refresh our memory and see how the word cloning fit into Java world.
What is cloning ?
"In biology, cloning is the process of producing similar populations of genetically identical individuals that occurs in nature when organisms."
-- Wikipedia
Here the term "genetically identical" need attention for Java developers for doing cloning of objects. We will look into the details later.
Java provide a method which help us to create "genetically identical" copy of object. It is achieved through clone() method, which is inside Object class.
Now lets see why Java provide a method to create object. If we create a new object then the state of the object is initialized, but what if we need a current state of object but at the same time we didn't want to disturb the current object.
For Example :-
Suppose you have an object X which is a singleton object and shared across application. In this scenario suppose a module need an object of X which will be changed the state of the object temporally but this will affect other module also. In this kind of scenario we need a clone of object.
How to clone an object ?
We can clone only those classes object which implements the Cloneable interface else it will result into CloneNotSupportedException exception.
Cloneable interface is a markup interface like Serializable interface. Cloneable interface is used to indicate that a class allows a bit wise copy of an object to be made.
Please note clone method does not invoke the constructor of target.
Simple example of Cloning.
Clone.java
- /**
- * @Author Anindya Bandopadhyay
- *
- * com\ch1\clone\Clone.java
- *
- * @Created on Jun 22, 2015 5:49:02 PM
- */
- package com.ch1.clone;
- public class Clone implements Cloneable{
- @Override
- public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
- return super .clone();
- }
- public Object cloneThis(){
- Object object = null;
- try {
- object = clone();
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return object;
- }
- }
CloneTester.java
- /**
- * @Author Anindya Bandopadhyay
- *
- * com\ch1\CloneTester.java
- *
- * @Created on Jun 22, 2015 10:51:40 AM
- */
- package com.ch1.clone;
- public class CloneTester {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Clone actual = new Clone();
- Clone clone = (Clone) actual.cloneThis();
- System.out.printf("Is both object are same ? %s",(actual == clone));
- }
- }
Output of the source code
Is both object are same ? false
Is both object are same ? false
As I earlier mention that we need to pay special attention to "genetically identical". Genetically identical means even if by cloning an object we get a new object but this new object will hold same data and/or object references.
This objects are known as Shallow Copy Object. While using cloning we have to be very careful as this shared object references between actual and clone object.
To mitigate this shared object references we use another technique which is known as Deep Copy Object. In this technique we create new object and copy the values, so that it will not interfere each others object processing.
Just think of the situation where we have a shared I/O object between two objects, where one is trying to writing something into it and another is trying to close it.This kind of situation leads to catastrophe in running environment because of this in Object class clone() method is protected so that if developer cannot simple clone an object. It must be overridden carefully and used by a different public method.
Lets see how Shallow and Deep copy objects references works.
Shallow Copy Object is achieved by simple invoking super.clone() method.
Shallow Copy Object is achieved by simple invoking super.clone() method.
ShallowClone.java
- /**
- * @Author Anindya Bandopadhyay
- *
- * com\ch1\clone\ShallowClone.java
- *
- * @Created on Jun 15, 2015 2:24:22 PM
- */
- package com.ch1.clone;
- public class ShallowClone implements Cloneable {
- private Object obj1;
- private int count;
- public ShallowClone(){
- obj1 = new Object();
- count = 1;
- System.out.println("Default constructor of CloneImpl.");
- }
- public ShallowClone(Object obj1,int size){
- this.obj1 = obj1;
- this.count = size;
- System.out.println("CloneImpl(InnerCloneObject obj1,int size) constructor of CloneImpl.");
- }
- public Object getObj1() {
- return obj1;
- }
- public void setObj1(Object obj1) {
- this.obj1 = obj1;
- }
- public int getCount() {
- return count;
- }
- public void setCount(int count) {
- this.count = count;
- }
- protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
- return super.clone();
- }
- public ShallowClone cloneThisObject(){
- ShallowClone object = null;
- try {
- System.out.println("\n======================= Start Clone ============================");
- object = (ShallowClone) clone();
- System.out.println("======================= End Clone ============================");
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return object;
- }
- }
Deep Copy Object is need to be take care by developer. clone() method is override with respect to specific requirement.
Please note this can be achieve even without overriding the clone() method also. We can simple put the logic directly inside cloneThisObject() method.
Please note this can be achieve even without overriding the clone() method also. We can simple put the logic directly inside cloneThisObject() method.
DeepClone.java
- /**
- * @Author Anindya Bandopadhyay
- *
- * com\ch1\clone\DeepClone.java
- *
- * @Created on Jun 19, 2015 12:12:26 AM
- */
- package com.ch1.clone;
- public class DeepClone implements Cloneable {
- private String name;
- private Object obj1;
- public DeepClone(){
- name = "Andy";
- obj1 = new Object();
- System.out.println("Default constructor of InnerCloneObject.");
- }
- public DeepClone(String name,Object obj1){
- this.name = name;
- this.obj1 = obj1;
- System.out.println("InnerCloneObject(String name,Object obj1) constructor of InnerCloneObject.");
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public Object getObj1() {
- return obj1;
- }
- public void setObj1(Object obj1) {
- this.obj1 = obj1;
- }
- protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{
- // Customize clone logic is placed.
- System.out.println("\n======================= Start Clone ============================");
- DeepClone object = new DeepClone();
- System.out.println("======================= End Clone ============================");
- return object;
- }
- public DeepClone cloneThisObject(){
- DeepClone object = null;
- try {
- object = (DeepClone) clone();
- } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return object;
- }
- }
Lets upgrade CloneTester class for Shallow and Deep copy objects.
CloneTester.java
- /**
- * @Author Anindya Bandopadhyay
- *
- * Chapter1\com\ch1\CloneTester.java
- *
- * @Created on Jun 22, 2015 10:51:40 AM
- */
- package com.ch1.clone;
- public class CloneTester {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ShallowClone shallowActualObject = new ShallowClone();
- DeepClone deepActualObject = new DeepClone();
- ShallowClone shallowCloneObject = shallowActualObject.cloneThisObject();
- DeepClone deepCloneObject = deepActualObject.cloneThisObject();
- System.out.printf("Is ShallowClone actual object are different from clone object ? %s ",
- (shallowActualObject != shallowCloneObject));
- System.out.printf("\nIs object inside ShallowClone object are different ? %s \n",
- (shallowActualObject.getObj1() == shallowCloneObject.getObj1()));
- System.out.printf("Is DeepClone actual object are different from clone object ? %s ",
- (deepActualObject != deepCloneObject));
- System.out.printf("\nIs object inside DeepClone object are different ? %s ",
- (deepActualObject.getObj1() == deepCloneObject.getObj1()));
- }
- }
Output of the source code
Default constructor of ShallowClone.
Default constructor of DeepClone.
======================= Start Clone ============================
======================= End Clone ============================
======================= Start Clone ============================
Default constructor of DeepClone.
======================= End Clone ============================
Is ShallowClone actual object are different from clone object ? true
Is object inside ShallowClone object are different ? true
Is DeepClone actual object are different from clone object ? true
Is object inside DeepClone object are different ? false
Shallow Copy Object Graph
Default constructor of ShallowClone.
Default constructor of DeepClone.
======================= Start Clone ============================
======================= End Clone ============================
======================= Start Clone ============================
Default constructor of DeepClone.
======================= End Clone ============================
Is ShallowClone actual object are different from clone object ? true
Is object inside ShallowClone object are different ? true
Is DeepClone actual object are different from clone object ? true
Is object inside DeepClone object are different ? false
Shallow Copy Object Graph
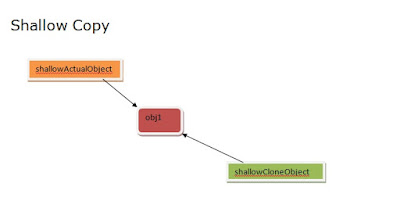 | |||
| Shallow Copy Object |
Just compare the outputs and object graphs. By these we can deceive that how important for developer to pay attention to need of cloning or overriding the clone() method.
If you have any question or feedback please comment.
If you have any question or feedback please comment.
