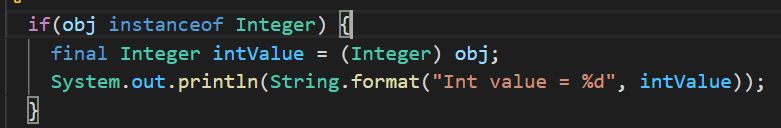
When we run a Spring Boot application we see a Spring Boot banner. I wonder if we could able to change this or not and find out that Spring gives us the opportunity to change it. Why anyone should do that? Answer will be just for fun and learning.
spring.application.name=My Custom Banner
spring.banner.location=classpath:myBanner.txt
Now let's run the Spring Boot application and see the result.
Now we will see how to use an image (*.png/*.jpg/*.gif) as a banner.
To implement image we need to get an image of *.png/*.jpg/*.gif type and put it into the class path and set the path in the Spring Boot property spring.banner.image.location=classpath:myBanner.png here my image file name is myBanner.png.
- spring.main.banner-mode where we mention the banner mode console | log | off and the default value is console. console will print the banner in console and log in log file and off will turn of the banner.
- spring.banner.image.location where we put the banner image file location and the default value is classpath:banner.gif.
- spring.banner.image.height where we put an integer to specify the height of the image and the default value will be based on the image height.
- spring.banner.image.width where we put an integer to specify the width of the image in chars and the default value is 76.
- spring.banner.image.margin where we put an integer to specify the margin from the left hand image margin in chars and the default value is 2.
- spring.banner.image.bitdepth is used for ANSI colour and where we use two allowed values 4 (16 colour) or 8 (256 colour).
- spring.banner.image.invert is set to true then the dark terminal themes will be used for and the default value is false.
- spring.banner.image.pixelmode is to determine the pixel used to render the image, where we can use TEXT | BLOCK and the default value is TEXT. TEXT will use ' ', '.', '*', ':', 'o', '&', '8', '#', '@' to render image and BLOCK will use ' ', '░', '▒', '▓', '█' to render image.
spring.application.name=My Custom Banner
spring.main.banner-mode=console
spring.banner.location=classpath:myBanner.txt
spring.banner.image.pixelmode=text
spring.banner.image.location=classpath:myBanner.png
spring.banner.image.height=10
spring.banner.image.width=30
spring.banner.image.margin=2
spring.banner.image.bitdepth=8
spring.banner.image.invert=false
I will be using this 32 bit colour myBanner.png
 |
| myBanner.png |
 |
| Banner as a TEXT |
 |
| Inverted image render |
 |
| Banner as a BLOCK |
 |
| Banner in log file |